As the largest internet service provider in the US, Comcast has taken it upon itself to develop greener and more sustainable internet for the future. It has been working on new technologies to grow its 10G network more sustainably. Comcast’s efforts are making Xfinity more widely available, enabling faster broadband speeds, and lowering the cost and energy requirements for data transmission for Mbps.
Just recently, Comcast was recognized for its work on virtual Cable Modem Termination Systems (vCMTSs) by the National Academy of Television Arts and Sciences and was given an Emmy Award for Technology and Engineering. Deployment of vCMTSs is a key constituent of Xfinity’s 10G Network that is already bringing down energy costs of scaling networks and meeting tomorrow’s traffic demands sustainably. In fact, can get a connection on the 10G Network with the help of Xfinity customer service that’s already using vCMTSs.
The vCMTS technology involves the virtualization of CMTS. Before we talk about how vCMTS technology makes the internet greener, we first need to understand what a CMTS is and what it does in the first place.
What Does A CMTS Do?
A Cabel Modem Termination System is a type of router located at a broadband company’s headend. CMTSs communicate with your modem as well as all the other modems connected to the same switch. Here’s the problem it created to solve:
Cable Networks Weren’t Originally Designed For the Internet
Cable Internet uses cable networks that were first put in place for cable TV. All TVs show the same live video and receive the same data from the cable company. This is why the cable coming to your home doesn’t connect to the cable company’s headend directly. A switch combines the cables from all the neighboring houses that are using the same cable company. A single coaxial cable runs to the cable company’s headend.
This means that the cable company can’t send a data packet to your house directly. Anything sent from the company’s headend travels to the switch, which sends it to all the houses in the network.
An even bigger problem is with sending data to the cable company. The headend has no way of knowing and verifying which modem and house the data is coming from—the switch combines all upstream signals into one. The following diagram shows a cable network transmitting upstream data to a cable head end.
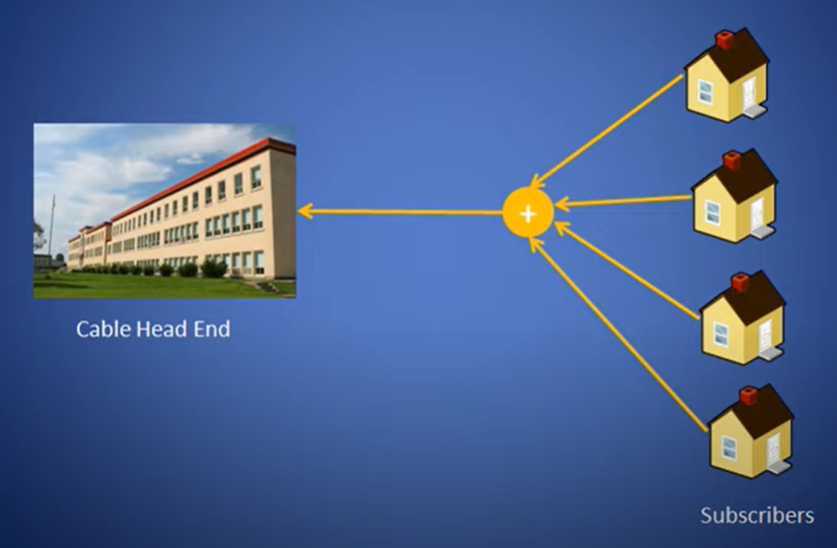
Alt Attribute: Diagram showing upstream data to the CMTS at the cable headend
CMTS Works With Your Modem to Manage Downstream and Upstream Data
The CMTS manages all the modems in all the houses in your area that use the same service provider. It assigns different frequency ranges to different modems. Only your modem reads the data in the frequency range assigned to you. All other modems ignore it.
The CMTS also sends timing information every 30 seconds. It tells your modem precisely when to send data upstream, no other modem can send data in the slot assigned to your modem. This is how it distinguishes between upstream data sent from different modems.
What is vCMTS Technology?
Virtualization is everywhere in IT right now and it has completely changed how we work. vCMTS are virtual CMTS. To understand what that means, let us briefly explain virtualization and virtual machines (VMs).
Virtualization and Virtual Machines
The device you’re reading this article on right now is running an operating system. It could be MacOS, Windows, iOS, Android, etc. If you want to install another OS on your existing device, you can do it by creating a virtual machine.
Virtual machines are created using a type of software called a hypervisor. The hypervisor allocates some of your computer’s resources (memory, space, etc) to a virtual machine on which you can install a new OS. The OS doesn’t know that it’s not on a virtual machine and it works exactly the same as it would on a real machine
You can also create multiple virtual machines each with its own OS on the same computer. The different VMs will have no knowledge of each other’s existence. They wouldn’t be directly connected to each other in any way even though they’re on the same device. It would be as if you have multiple devices.
vCMTS Technology and How it Increases Efficiency
One CMTS can serve anywhere between 4,000 to 150,000 modems. To expand a network, more CMTSs are needed to be assembled and maintained. This takes a lot of time and hard work. CMTSs also take up space and consume a lot of power directly and for HVAC.
Virtual CMTSs are multiple CMTSs running on the same hardware. When a new CMTS is needed, it can be created virtually with no extra investment in the assembly and maintenance of a legacy CMTS. Only the existing hardware needs to have enough resources available. According to an estimate, 60,000 homes need 20 racks of legacy CMTSs, which can be replaced by just two racks of vCMTSs.
Comcast Xfinity Internet Delivers the Best Value for Money
Comcast recently reported 36% energy efficiency gains for the 10G network in 2022 compared to 2019. The company aims to go carbon neutral by 2035 and is working to further increase efficiency and decrease the cost of the internet.
Xfinity is promoting its most exciting limited-time deal yet on the 10G Network. For $25 per month, you get 200 Mbps internet with WiFi equipment included. The offer also has a price lock for 2 years. Call Xfinity customer service at 844-343-1172 to learn more.

